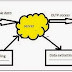
Dividing complex projects to simpler and manageable tasks is the process identified as Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
Usually,
the project managers use this method for simplifying the project
execution. In WBS, much larger tasks are broken down to manageable
chunks of work. These chunks can be easily supervised and estimated.
Following example is an outlined WBS:

There are many design goals for WBS. Some important goals are as follows:
- Giving visibility to important work efforts.
-
Giving visibility to risky work efforts.
-
Illustrate the correlation between the activities and deliverables.
WBS Structure:
In
a WBS diagram, the project scope is graphically expressed. Usually the
diagram starts with a graphic object or a box at the top, which
represents the entire project. Then, there are sub-components under the
box.
These
boxes represent the deliverables of the project. Under each
deliverable, there are sub-elements listed. These sub-elements are the
activities that should be performed in order to achieve the
deliverables.
Although
most of the WBS diagrams are designed based on the deliveries, some WBS
are created based on the project phases. Usually, information
technology projects are perfectly fit into WBS model.
Therefore, almost all information technology projects make use of WBS.
In addition to the general use of WBS,
there is specific objective for deriving a WBS as well. WBS is the input
for Gantt charts, a tool that is used for project management purpose.
Gantt chart is used for tracking the progression of the tasks derived by WBS.
Following is a sample WBS diagram: